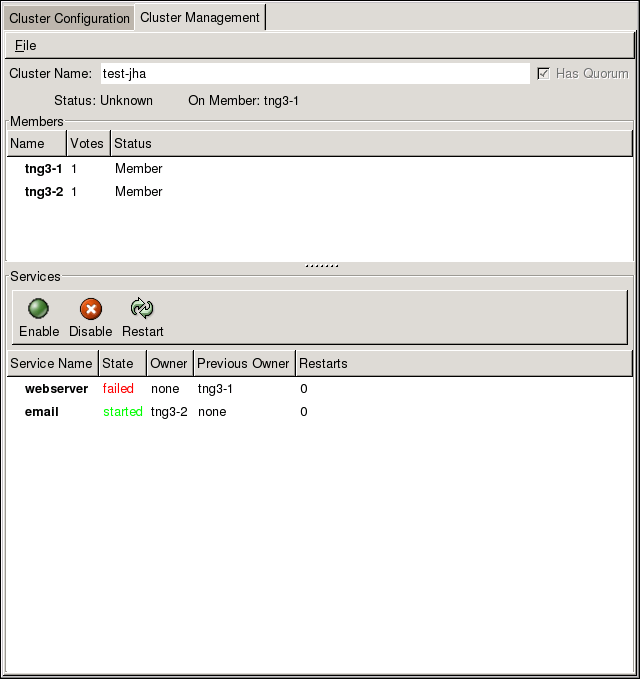
You can manage cluster services with the Cluster Status Tool (Figure 5.1, “Cluster Status Tool”) through the Cluster Management tab in Cluster Administration GUI.
You can use the Cluster Status Tool to enable, disable, restart, or relocate a high-availability service. The Cluster Status Tool displays the current cluster status in the Services area and automatically updates the status every 10 seconds.
To enable a service, you can select the service in the Services area and click Enable. To disable a service, you can select the service in the Services area and click Disable. To restart a service, you can select the service in the Services area and click Restart. To relocate a service from one node to another, you can drag the service to another node and drop the service onto that node. Relocating a service restarts the service on that node. (Relocating a service to its current node — that is, dragging a service to its current node and dropping the service onto that node — restarts the service.)
The following tables describe the members and services status information displayed by the Cluster Status Tool.
| Members Status | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Member |
|
||
| Dead | The node is unable to participate as a cluster member. The most basic cluster software is not running on the node. |
Table 5.1. Members Status
| Services Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Started | The service resources are configured and available on the cluster system that owns the service. |
| Pending | The service has failed on a member and is pending start on another member. |
| Disabled | The service has been disabled, and does not have an assigned owner. A disabled service is never restarted automatically by the cluster. |
| Stopped | The service is not running; it is waiting for a member capable of starting the service. A service remains in the stopped state if autostart is disabled. |
| Failed | The service has failed to start on the cluster and cannot successfully stop the service. A failed service is never restarted automatically by the cluster. |
Table 5.2. Services Status